About recovery
How to measure cardio recovery on Apple Watch
Apple Watch automatically tracks cardio recovery after several outdoor workouts. Outdoor running, outdoor hiking, or outdoor walking all count. Just make sure the watch stays on for three minutes after the workout is over.
How Apple Watch calculates cardio recovery
Apple Watch’s cardio recovery metric estimates how many BPM your heart rate falls one minute after the workout ends. For example, if your peak heart rate during the workout is 150 bpm, and 1 minute after the workout it’s 100 bpm, then your cardio recovery is 50 bpm. Some Garmin watches, like the Forerunner 935 and Forerunner 955, calculate HRR at two minutes.
What’s a good cardio recovery?
A cardio recovery of 12 beats or more is generally considered normal. A cardio recovery of 43 bpm would put you in the top 10% (for people under the age of 35). For those at 65+, the 90th percentile is 25bpm for women and 19 bpm for men.
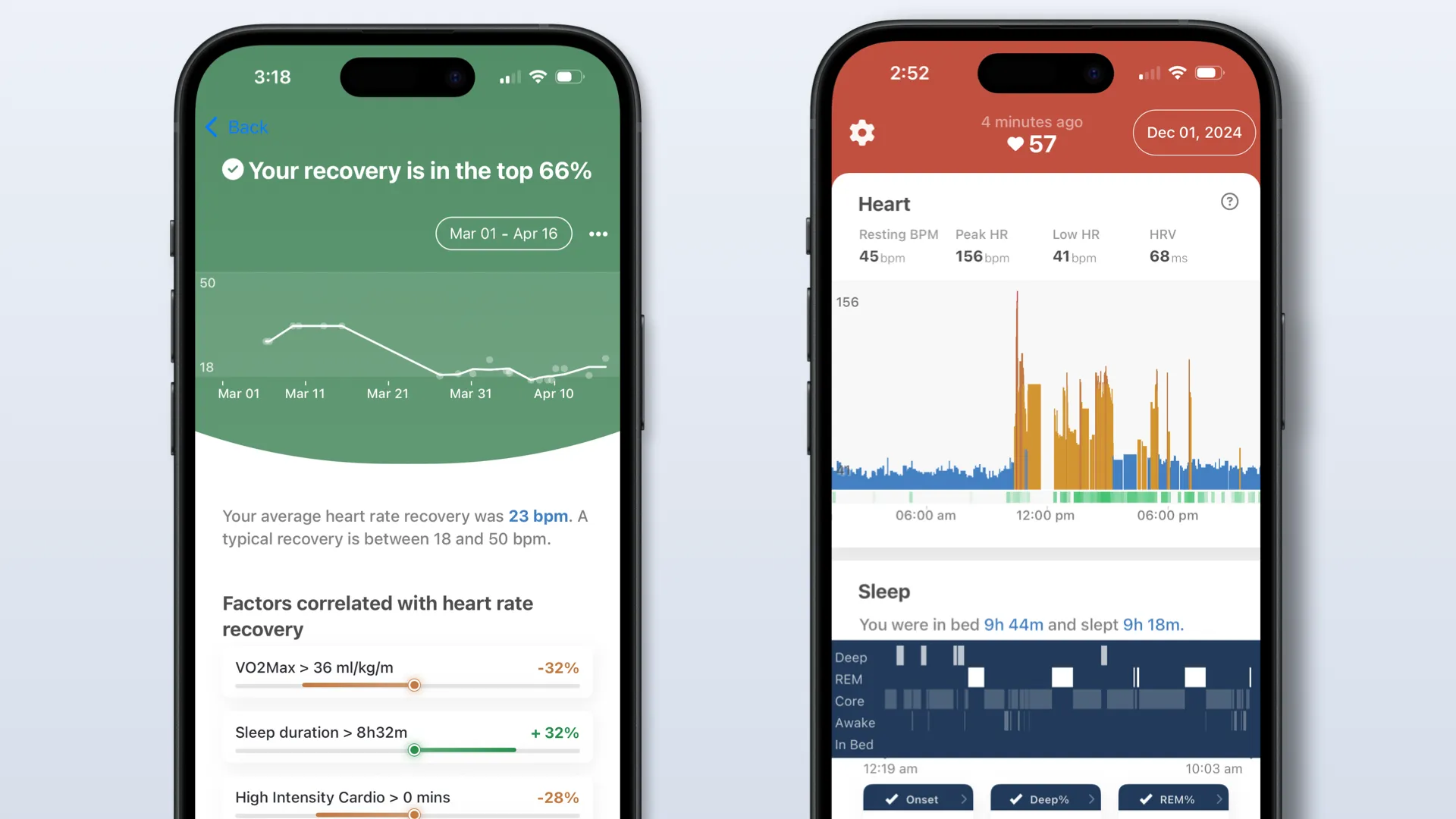 You can benchmark your cardio recovery in Empirical Health for Apple Watch
You can benchmark your cardio recovery in Empirical Health for Apple Watch
Cardio recovery vs heart rate recovery
Cardio recovery is a synonym for heart rate recovery. “Cardio recovery” is the term used in the Apple Watch and the Health app. “Heart rate recovery” is the term more common in the medical literature. Either way, it measures the rate that your heart rate drops back to normal after exercise. Apple Watch estimates heart rate recovery one minute after exercise, but 1-, 2, or 3-minute intervals are common in the medical literature.
Causes of low cardio recovery
Low cardio recovery is often caused by a prior heart attack, autonomic conditions like POTS, or lack of exercise.
- After a heart attack, cardio recovery is often initially lower. Cardiac rehabilitation programs use structured, gradual exercise to gradually increase the strength of your heart muscle. Often heart rate recovery is used as a key predictor of whether you will be rehospitalized.
- Autonomic conditions, like POTS, can cause lower cardio recovery. POTS testing often involves tracking changes in heart rate after standing, such as in the Poor man’s tilt table test
- Lack of exercise can cause low cardio recovery.
How to improve heart rate recovery
You can improve heart rate recovery with exercise, particularly zone 2 and zone 5 training. Common workouts are Low-Intensity Steady-State (LISS) Cardio, HIIT (High-Intensity Interval Training), Fartlek Training, and Circuit Training. Compared to workout routines that improve VO2Max, the workout routines that improve cardio recovery tend to involve more submaximal exercise (zone 2).
How to use cardio recovery as part of a comprehensive heart health program
 Comprehensive heart health involves both Apple Watch metrics and advanced blood test metrics for heart health
Comprehensive heart health involves both Apple Watch metrics and advanced blood test metrics for heart health
A comprehensive heart health program requires tracking metrics of the heart’s pump, electrical system, and power supply:
- Overall cardiovascular fitness (“pump”) — includes Apple Watch metrics like VO2Max, resting heart rate, and cardio recovery.
- Heart attack risk (“power supply”) — the Apple Watch does not measure heart attack risk, but a blood test can, including advanced metrics like ApoB.
- Heart rhythm (“electrical system”) — Apple Watch’s ECG sensor can detect atrial fibrillation and other abnormal heart rhythms.
How cardio recovery, HRV, resting heart rate, and VO2 Max are correlated
Cardio recovery, HRV, resting heart rate, and VO2 max are highly correlated on Apple Watch.
This is because they’re tracking two physiological processes. HRV mostly tracks the autonomic nervous system (ANS). VO2Max mostly tracks the volume of blood your heart muscle can pump. Cardio recovery and resting heart rate measure a blend of the two.
See more information on our guide to Apple Watch’s cardio fitness metric, autonomic nervous system, and explanation of how Apple Watch uses heart rate and GPS to estimate VO2 Max.
What to do if you have no cardio recovery data
If you see no cardio recovery data on Apple Watch, check your workouts. You need:
- Multiple outdoor workouts (hiking, running, walking, etc)
- …on flat ground (5% grade or less).
- …with GPS turned on. Take your phone with you if your watch does not have GPS.
You don’t have to reach your peak heart rate in order to estimate cardio recovery, but you do need outdoor workouts on flat ground with GPS. All Apple Watch models support heart rate recovery, including the Apple Watch Series 11, Ultra 3, and SE3 models released in 2025.






