About REM sleep
What is REM sleep?
If deep sleep restores the body, then REM sleep restores the mind.
REM (Rapid Eye Movement) sleep is a stage of sleep where your eyes move quickly, dreams are vivid, and brain activity is high, almost like when you’re awake. During this time, your body is mostly paralyzed to stop you from acting out dreams. REM is important for memory, learning, and mood, and becomes longer in the later parts of the night.
Sleep stages was launched in WatchOS 9. Apple Watch Series 4 or later, including the Apple Watch SE3 (2025), works with sleep stages.
How accurate is Apple Watch’s sleep tracker
Apple developed their sleep stage algorithm using data from 858 volunteers, and then tested its accuracy on a separate set of 166 people who wore both an Apple Watch and medical PSG (polysomnography) equipment.
Apple Watch is about 78% accurate in detecting REM sleep. The most common error was confusing REM sleep for core sleep (21% of the time). It rarely confused REM sleep for deep sleep and wake (<1% of the time each).
This is the full confusion matrix, showing the true sleep stage (rows) vs the Apple Watch’s predicted sleep stage (columns):
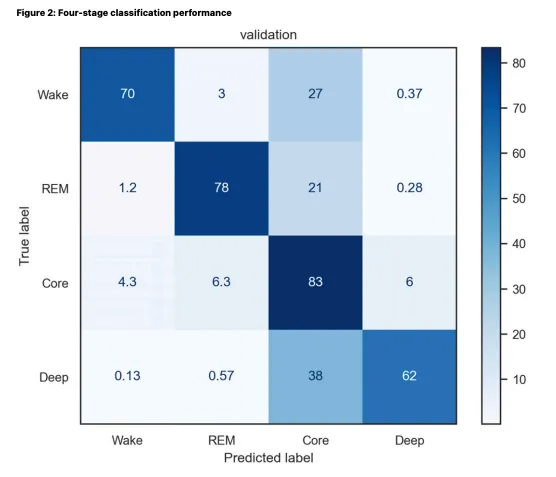
Does Apple Watch understimate REM sleep?
Apple Watch understimates REM sleep slightly. About 21% of REM sleep was incorrectly classified as core sleep.
How to measure REM sleep on your Apple Watch
All sleep stages-including REM—are automatically tracked as long as you sleep with your watch on for longer than 4 hours. You may need to set up a sleep schedule and turn on sleep tracking.
REM vs core vs deep sleep on Apple Watch
REM sleep restore the mind. Deep sleep restores the body. And core sleep is everything else. We wrote more on the science of Apple Watch sleep stages here, including normal amounts of deep and REM sleep.
How much REM sleep do you need?
About 20% of sleep each night should be REM sleep. Empirical Health has a daily sleep reports where you can see your sleep stages over time, as well as a comprehensive health score to compare your REM and deep sleep to others.
 Apple Watch sleep stages data shown in Empirical Health for Apple Watch.
Apple Watch sleep stages data shown in Empirical Health for Apple Watch.
Can low REM sleep be a sign of sleep apnea?
Yes, low REM can be a sign of sleep apnea. You can talk with an Empirical Health doctor about sleep apnea testing by booking an appointment.
What is core sleep?
Core sleep is any sleep that’s neither deep nor REM. It’s also called “light sleep,” and corresponds to non-REM sleep stages 1 and 2. While REM sleep and deep sleep both have targets of how much to get, there’s no target for core sleep, i.e., it is not worth optimizing your core sleep—focus on REM and deep instead).








