About Oxygen
The blood oxygen sensor was launched in 2020 with the Apple Watch Series 6, was disabled in Jan 2024 in the US due to a patent dispute, and was re-enabled on Aug 14, 2025.
Apple Watch Series 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, and 11, and the Apple Watch Ultra, Ultra 2, and Ultra 3 have oxygen sensing hardware. The Apple Watch SE series does not have a blood oxygen sensor (as of Aug 2024).
“Blood oxygen”, “oxygen saturation”, and “SpO2” are synonyms.
How the Apple Watch measures your blood oxygen saturation
Oxygenated and deoxygenated blood absorb red and infrared light differently. This lets an optical sensor at the back of the Apple Watch pick up subtle signs of oxygen saturation in your blood.
Both optical heart rate and oxygen sensors operate using the same principles: they shine light of a specific wavelength into your skin, and measure the light reflected back. Heart rate sensing uses both green light (525 nanometers) and infrared light (850-940 nanometers). Blood oxygen sensing adds a third red sensor (660 nanometers in wavelength).
On the third generation Apple heart rate sensor (used in the Series 6 and above), there are four groups of
photodiodes each with infrared, red, and green sensors, as well as additional infrared sensors (of a slightly
different wavelength) in the middle. They’re arranged in a pattern as shown below:
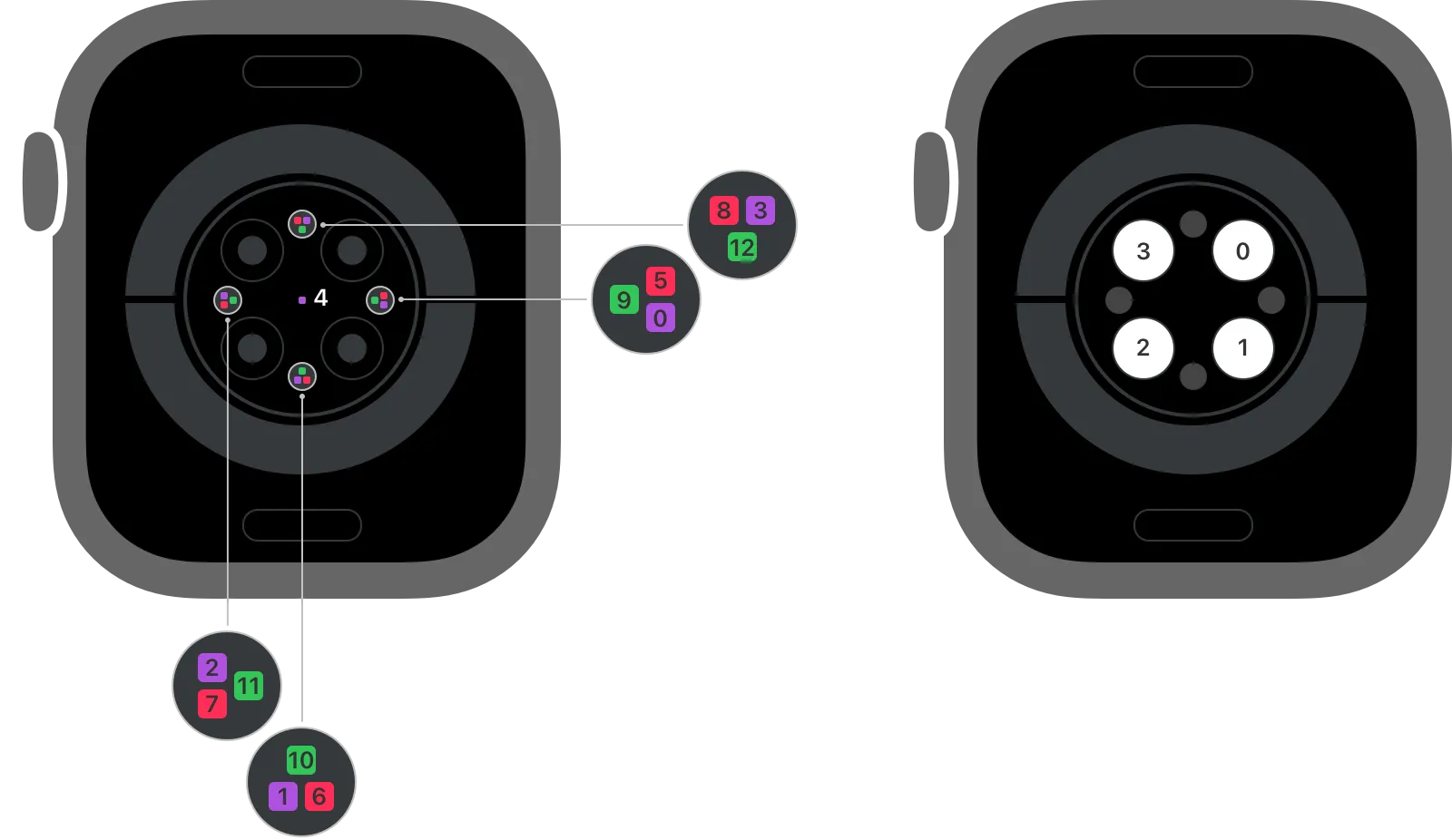
To estimate blood oxygen, the Apple Watch software calculates a ratio of absorbed red light to absorbed infrared light, and then combines them with some calibration constants derived from experimental data to estimate a percentage. This percentage is your blood oxygen saturation. A normal blood oxygen saturation is 95% or above.
Source: Apple’s developer documentation on SensorKit.
How accurate is Apple Watch’s blood oxygen sensor?
One research study showed the Apple Watch’s blood oxygen sensor is as reliable as a medical grade device. The study showed that the average absolute difference between Apple Watch and a medical-grade oximeter was less than 1%. So is blood oxygen on apple watch accurate? Yes. The researchers concluded that the Apple Watch’s oxygen sensor can “reliably detect states of reduced blood oxygen saturation”.
However, there are caveats. Studies have shown medical-grade pulse oximeters can over-estimate oxygen stauration for people with darker skin pigmentation. In Feb 2024, the FDA issued a draft document on performance evaluation of pulse oximeters taking into consideration skin pigmentation, race, and ethnicity; as of October 2024, new FDA guidelines were expected to be issued but have not been.
Oxygen saturation trends are more important than individual outliers
Blood oxygen saturation is inherently a noisy measurement. Trends matter more than individual points.
Even for “medical-grade” oxiemeters, the error bounds for individual measurements are quite wide. To get an FDA clearance, about 95% of oxygen values must fall within 4-6% of the gold-standard value. This means if you see an SpO2 of 92%, the true value is likely between 88% and 96%.
How to update your Apple Watch to get oxygen saturation
To get oxygen measurements, update your iPhone to iOS 18.6.1 and Apple Watch to watchOS 11.6.1. Once you update, you will be able to see oxygen readings in the Health app on your iPhone. (You won’t be able to see oxygen readings directly on your Apple Watch.) If you do not initially see oxygen measurements, open the ECG app on your watch to trigger the sensor.
Why was the oxygen sensor disabled in 2024
The oxygen sensor was disabled in 2024 due to a patent dispute (but is now available). The U.S. International Trade Commission (ITC) ruled that Apple’s blood oxygen sensor infringed on patents of Masimo, leading to a potential import ban. In order to comply with the ruling and continue selling watches in the United States, Apple disabled the sensor via a firmware update on January 18, 2024. New Apple Watches are still being manufactured with the sensing hardware. If you buy a new Apple Watch in the US, it will have the oxygen sensor hardware, but it will be disabled in software. The patents under dispute expire in 2028.
How the sensor came back in 2025
On Aug 14, 2025, Apple announced the blood oxygen sensor was coming back. They were able to re-launch oxygen sensing due to a new implementation that measures light using the Apple Watch’s sensors, but performs calculations on the iPhone.
What low blood oxygen levels mean
Normal oxygen saturation levels are 95% to 100%. Oxygen saturation levels below 90% are considered abnormal.
If your blood oxygen saturation is low, some likely causes are sleep apnea, high altitude, a covid infection, a chronic condition like asthma or COPD.
Sleep apnea and blood oxygen time below 90%
While the Apple Watch’s breathing disturbance feature uses the accelerometer, not blood oxygen, low blood oxygen during sleep can be a sign of sleep apnea. In our analysis of sleep apnea vs Apple Watch health signals, low sleeping blood oxygen was the #1 predictor of sleep apnea. The variance in oxygen readings was the #4 predictor. Low REM sleep, low cardio recovery, and high respiratory rate rounded out the top 5 signals of sleep apnea risk.
Talk with a doctor about sleep apnea testing if you suspect sleep apnea.
Covid infection and low blood oxygen
A COVID infection can reduce blood oxygen levels due to lung inflammation, fluid buildup, ARDS, and potential long-term damage to lung tissue, as well as increased risk for blood clots.
COPD or asthma and oxygen levels
Asthma and COPD flare-ups, often triggered by infections or pollutants, can significantly worsen oxygen levels, necessitating supplemental oxygen or hospitalization.
High altitude can cause low oxygen levels
Your blood oxygen may drop if you travel to a place at high altitude. It may take several days to acclimate. Even after acclimation, your blood oxygen level may be lower than the standard range.
Other lung and heart conditions
For example, heart failure, pulmonary edema (fluid accumulation in the lungs), pulminary embolism (a blood clot in the lungs, which is a medical emergency), anemia (sometimes caused by low iron), and other health conditions may cause low blood oxygen. Check with your doctor if you have concerns.






